A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack is an attempt to shut down a machine or a network through multiple infected computer systems. The main goal of this attack is to make an online service unavailable or disrupt the legitimate traffic of a targeted server by overwhelming it with bad bot traffic. It is one of the most common and disruptive types of cyber-attack.
How Does a DDoS Attack Work
Firstly, the attacker plans for a DDoS attack by exploiting vulnerabilities in one or more computer systems and making it a part of a botnet – where the attacker controls this botnet via centralized command and control (CnC) system. This master system identifies other vulnerable systems and gets control over them by infecting them and using them as zombie computers/bots.
Then the attacker targets a victim with all these infected bots (combinely “a botnet”) and floods the target’s internet pipe with multiple illegitimate requests sent via CNC, which causes a denial of service/unavailability to those legitimate requests that are trying to access the victim’s network/web resource.
DoS v/s DDoS Attacks
In a DoS attack, the attacker uses a single zombie computer to flood a network with TCP/UDP packets. The purpose of a DoS attack is to overload the targeted network’s bandwidth and other resources with illegitimate packets/requests. This will impact the unavailability of a targeted network to its legitimate users.
Wherein a DDoS attack, the attacker uses multiple zombie computers and multiple internet connections to overload the targeted network. In this attack, the targeted network is overloaded with hundreds or even thousands of requests at the same time.
Common Types of DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks are divided into three categories:-
- Application Layer Attacks (Connection-based):
The Application Layer attacks, also known as Layer 7 DDoS attacks, occur when an attacker targets a specific application or a website that is poorly coded in order to exploit its weakness. The attacker targets the layer where web pages are generated on the server and delivered in response to HTTP requests. These type of attacks are considered the most sophisticated and serious type of attacks.
Slowloris, slow post, and HTTP/S flood attacks are the type of application layer attacks.
Example:-

- Protocol Attacks:
The protocol attacks, also known as state exhaustion, the attacker targets the connection capacity of the web application servers, firewalls, and load balancers and utilizes the weaknesses in layers 3 and layer 4 of the protocols that are running concurrently to make a target’s service inaccessible.
ICMP Flood, Ping of Death and SYN Flood are the types of protocol attacks.
Example:-

- Volumetric Attacks (Connectionless):
The volumetric DDoS attack, also known as a flood attack is the type of attack where an attacker overwhelms the available internet bandwidth of a network by flooding it with a large volume of traffic requests sent via a botnet. Volumetric attacks are easy to generate by employing simple amplification techniques.
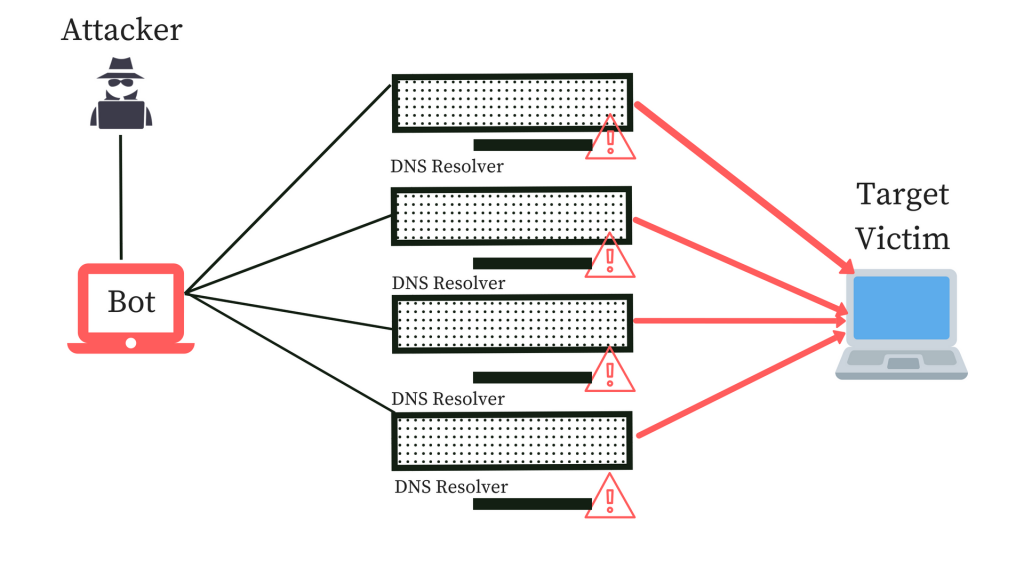
NTP Amplification, DNS Amplification, UDP Flood, and TCP Flood are the type of volumetric attacks.
Example:-
How to Protect against DDoS attacks
With the rise of botnets and DDoS attacks globally, it is important for every online business to have DDoS protection in place to mitigate service outage risks. The DDoS attacks create massive business risks for any enterprise small or large. Haltdos’s DDoS Mitigation Solution provide the highest level of network protection and proper mitigation techniques to prevent a variety of DDoS attacks from ever reaching the enterprise network and ensure 247365 uptime of online business operations.
Need help to protect your business from DDoS attacks and want to protect your web resources? Contact Us!




